
The rationale behind daylight saving time is that it would provide a person an extra hour of daylight after they've completed their daily activities, such as work or school. By adjusting the clock forward, the sun effectively rises later and, more importantly, sets later. Typically, this involves adjusting clocks 1 hour forward at the beginning of spring, then adjusting them back 1 hour in the fall. The practice originated to make darkness occur later in the day (based on a clock). For example, 10:30 AM in UTC can be written as "10:30 UTC" or "10:30Z." Daylight saving timeĭaylight saving time (DST) is a custom observed in certain countries or regions in which clocks are adjusted by an hour seasonally.

As an example, Central Standard Time is a timezone in the US that can be expressed as "UTC-06:00" or "UTC -6" while Japan Standard Time is expressed as "UTC+09:00" or "UTC +9." The time zone that uses UTC can be expressed as "UTC☐0:00".
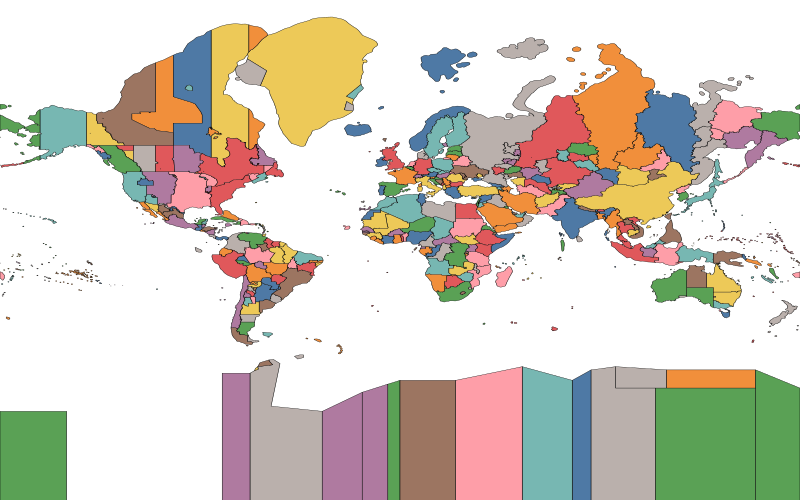
Similarly, a positive offset indicates a time zone east of 0° longitude. Most are offset by a whole number of hours, but some are offset by 30 or 45 minutes.Ī negative offset indicates that the time zone is west of 0° longitude. UTC is the chosen time standard, and time zones around the world are expressed as an offset of UTC. Mean solar time uses the length of an average day (24 hours), so time progresses at a constant speed, allowing us to create standardized time systems, such as UTC. If looked from the earth, the sun doesn't travel at a uniform speed throughout the year, so solar days vary in length, meaning that time doesn't progress at a constant speed when using true solar time. Solar time bases the passage of time on the position of the sun in the sky. To understand mean solar time, we first need to understand solar time. It is based on International Atomic Time, and is adjusted to be within 1 second of Universal Time, which is mean solar time at 0° longitude. UTC is the primary standard of time that has been used since 1961 to regulate clocks and time around the world. Below is an example of a map showing the world's time zones: Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) A country could also have borders that span multiple time zones, but be small enough that it would make more sense for the entire country to use a single time zone. While time zones generally change with respect to their longitude, they are not solely based on longitude for example, a country could fit in a different time zone based on longitude, but may have close ties to a neighboring country such that using the same time zone would be beneficial. Home / primary math / time / time zone Time zoneĪ time zone is a region of the Earth that follows a standard time, usually based on legal, commercial, and/or social reasons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
